Archives
- 2026-03
- 2026-02
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2018-07
-
br Activity and expression of aromatase in the
2025-01-22
Activity and expression of aromatase in the hippocampus The brain, like the adrenals, gonads and the placenta, is a steroidogenic organ. This paradigm emerged from studies carried out as early as the 1980s by Baulieu and co-workers; these studies showed that steroids such as pregnenolone and dehy
-
Recently competitive inhibitors of arginase have been develo
2025-01-22
Recently, competitive inhibitors of arginase have been developed which have greater specificity for the enzyme. Initial development of these compounds involved determination of the crystal structure of arginase. Christianson and colleagues found that a binuclear manganese cluster was required for ca
-
br Conflict of interest br Introduction Platelets
2025-01-22
Conflict of interest Introduction Platelets are anucleate blood cells essential for hemostasis and wound healing; tight regulation of platelet numbers is crucial for human health. Platelets are synthesized and released from bone marrow megakaryocytes into the circulation where they remain for
-
F is an orotomide a novel class of antifungals
2025-01-22
F901318 is an orotomide, a novel class of antifungals, which inhibits pyridine biosynthesis by blocking dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (URA1) activity [137]. Although this pathway is conserved in humans, human URA1 is only 20% identical to its fungal homolog and it is inhibited 2000-fold less effectiv
-
In the largest postmortem study
2025-01-21
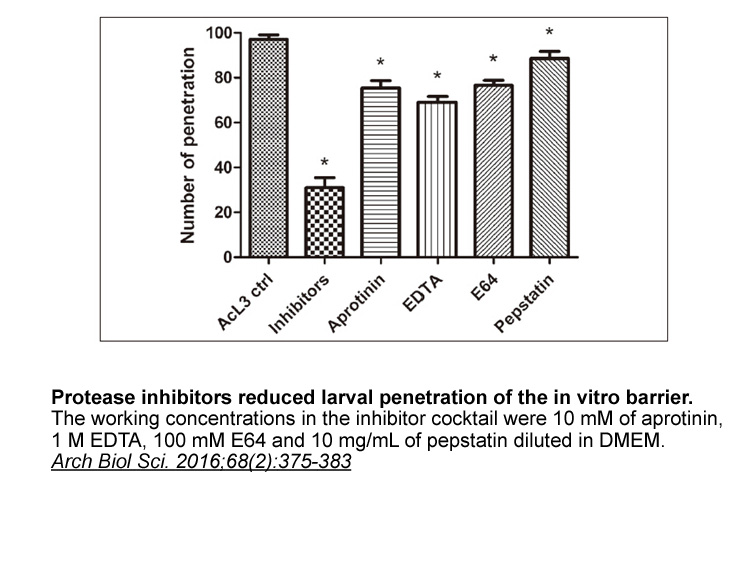
In the largest postmortem study of 3618 autopsied individuals, almost 75% of the individuals without Aβ pathology already harbored cortical NFT pathology mostly confined to the medial temporal regions (Murray et al., 2015). In Braak's study of 2366 autopsied individuals (Braak and Del Tredici, 2014
-
br Introduction Alcohol i e ethanol is
2025-01-21
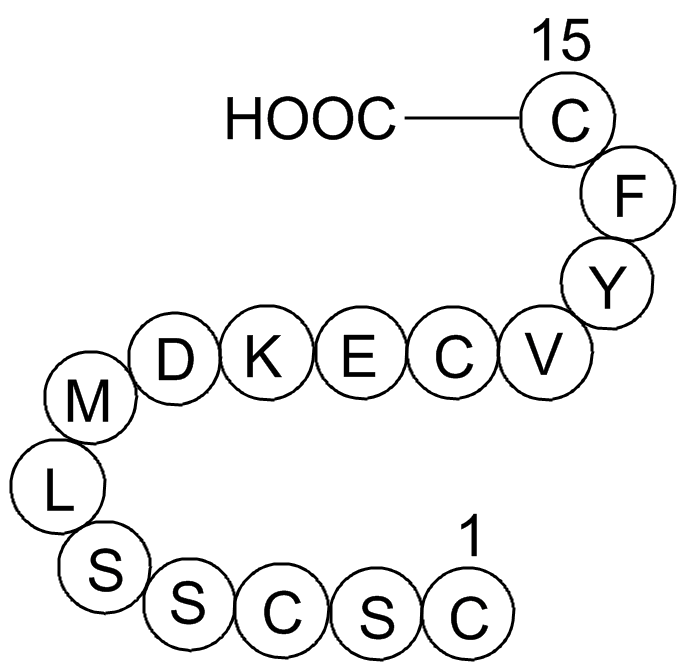
Introduction Alcohol, i.e., ethanol, is absorbed into the blood from the stomach to the small intestine, then distributed throughout the body. The metabolism of alcohol converting to acetic Biotin-binding beads basically involves two enzymes; alcohol dehydrogenase converting ethanol to acetaldeh
-
The role of circulating physiologic concentrations of FGF in
2025-01-21
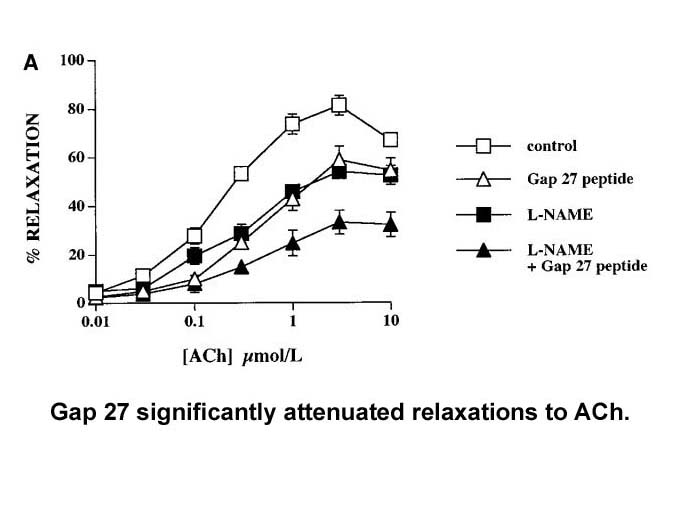
The role of circulating physiologic concentrations of FGF21 in glucose metabolism, however, remains unclear. Circulating FGF21 levels in obese and diabetic rodents, and in patients with type 2 diabetes are significantly higher than those in controls without diabetes [4], [5], [6]. On the other hand,
-
br Material and methods br Results br
2025-01-21
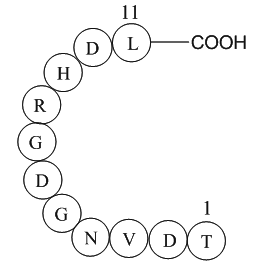
Material and methods Results Discussion GRK2 activity has increasingly been shown to contribute to the progression of numerous diseases and organ dysfunction [5], [6]. For instance, a large body of work over the last two decades has identified GRK2 as a major regulator of cardiac dysfunctio
-
We now present a series of
2025-01-21
We now present a series of findings obtained in heterologous expression systems, brain slices, and living animals that suggest that any interaction between mGlu7 and α1-adrenergic receptors exists, is specific, and is physiologically and behaviourally relevant. Materials and methods Norepinephri
-
There is a growing literature on ABCA expression in
2025-01-21
There is a growing literature on ABCA2 expression in human biopsies, where it has been described as a potential biomarker of leukemias. In childhood T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, ABCA2 and ABCA3 were expressed at high levels, which upon treatment with methotrexate, vinblastine and doxorubici
-
plumbagin Subsequently Palvimaki et al corroborated
2025-01-21
Subsequently, Palvimaki et al. (1999) corroborated Ni and Miledi's study by demonstrating that treatment with fluoxetine leads to 43% occupancy of the 5-HT2C receptors. Moreover, the affinity of fluoxetine for 5HT2C receptors (Ki 65 nM) is close to its affinity for 5-HT transporters (Ki 33 nM) (Ni a
-
It has been reported that HT R involves
2025-01-21
It has been reported that 5-HT2R involves in type 2 diabetes mellitus and 5-HT-induced IR [22,23]. The present study also demonstrated that it is 5-HT2R rather than other 5-HT receptors, including 5-HT1BR and 5-HT7R, in the liver that mediates HFD-induced abnormality of hepatic lipid metabolism, and
-
br ACK inhibitors Since ACK activation is correlated
2025-01-21
ACK1 inhibitors Since ACK1 activation is correlated with poor prognosis in various cancers, strong efforts are being directed by multiple groups towards developing highly potent and specific small molecule inhibitors targeting the ACK1 kinase. At least eight small molecule kinase inhibitors have
-
br Acknowledgments We thank the
2025-01-21
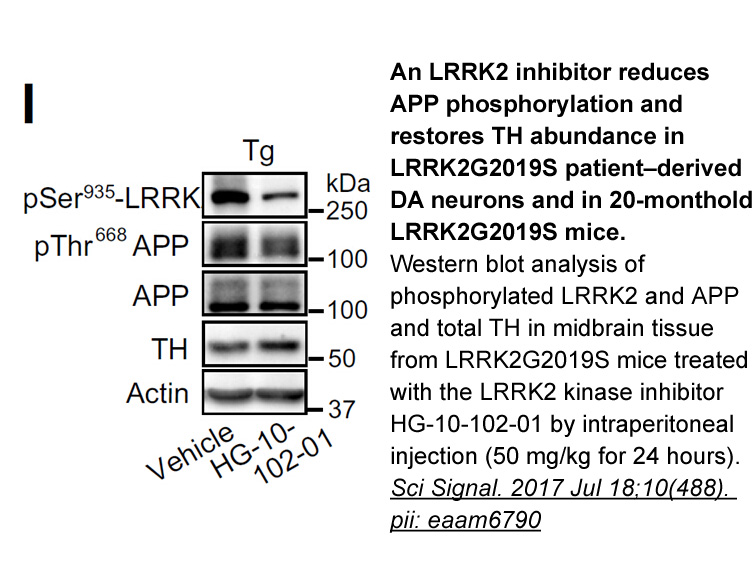
Acknowledgments We thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments on the manuscript, and also thank Dr. Hans-U. Dahms for his comments on the manuscript. This work was supported by a grant from the National Research Foundation (2009-0071218) funded to Young-Mi Lee. This work was al
-
During years research efforts at Los Alamos National Laborat
2025-01-21
During 2002–2004years research efforts at Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) focused on constructing a quantum computer based on regular arrays build from neutral radical molecules possessing one single unpaired SP2509 spin. The idea was built on the ability to manipulate individual electron spi
15281 records 34/1019 page Previous Next First page 上5页 3132333435 下5页 Last page